Introduction of MSIP
intro.RmdWorkflow
The main workflow for MSIP containing 3 steps:
- Construct atom tracing map based on MS fragmentation model.
- Acquire Multi-CE spectra and parse MS data to Fragment-Atom-Ratio map.
- Construct isotopomers contribution matrix and solve isotopomers by Non-linear program.
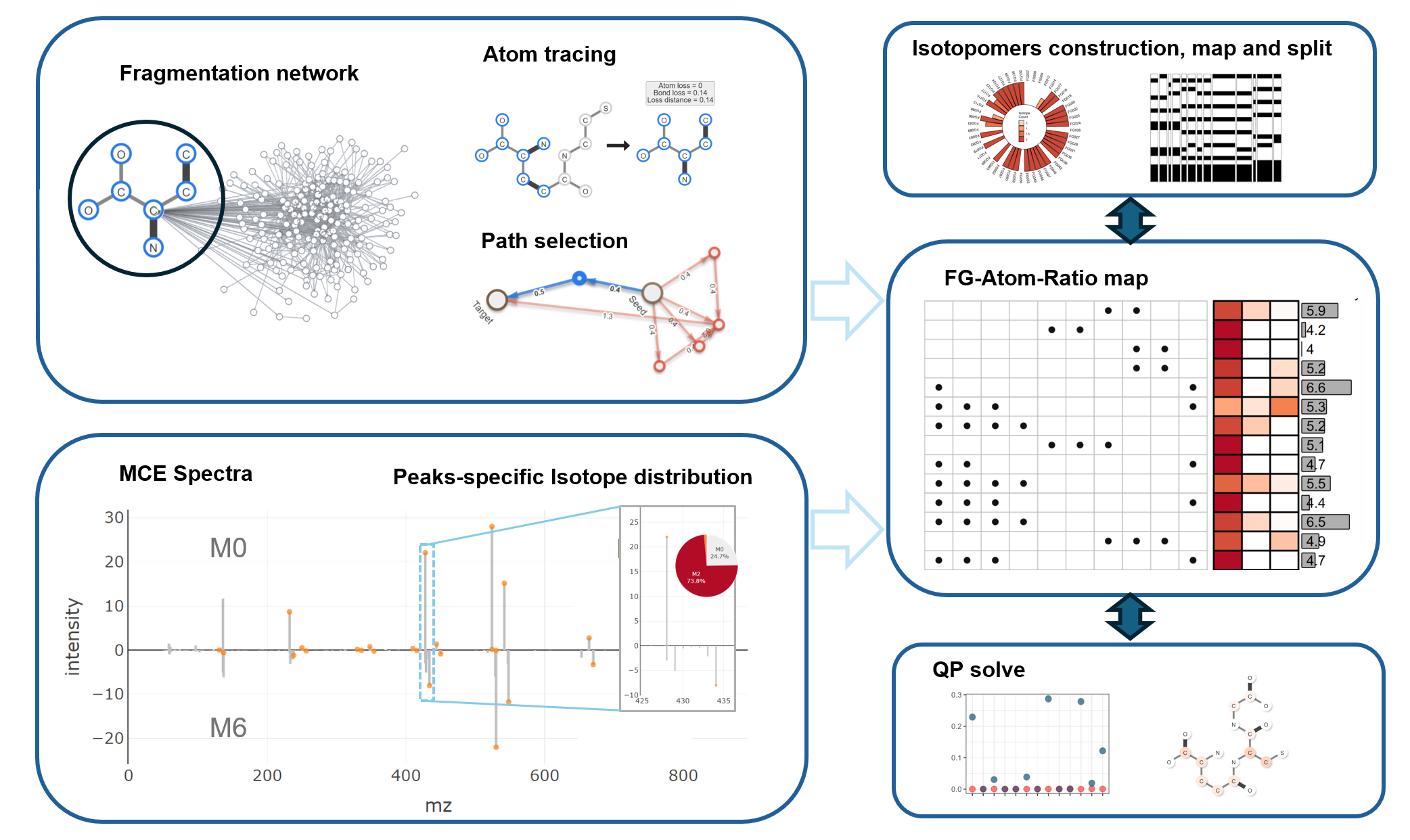
MSIP workflow
MSIP
Atom Tracing Map
Based on a MS fragmentation model (CFM), we develop a model to trace atoms in the process of MS fragmentation for a give metabolite molecule structure (SMILES).
Using this model, we could calculate the probability of fragments containing any atoms in the original molecule.
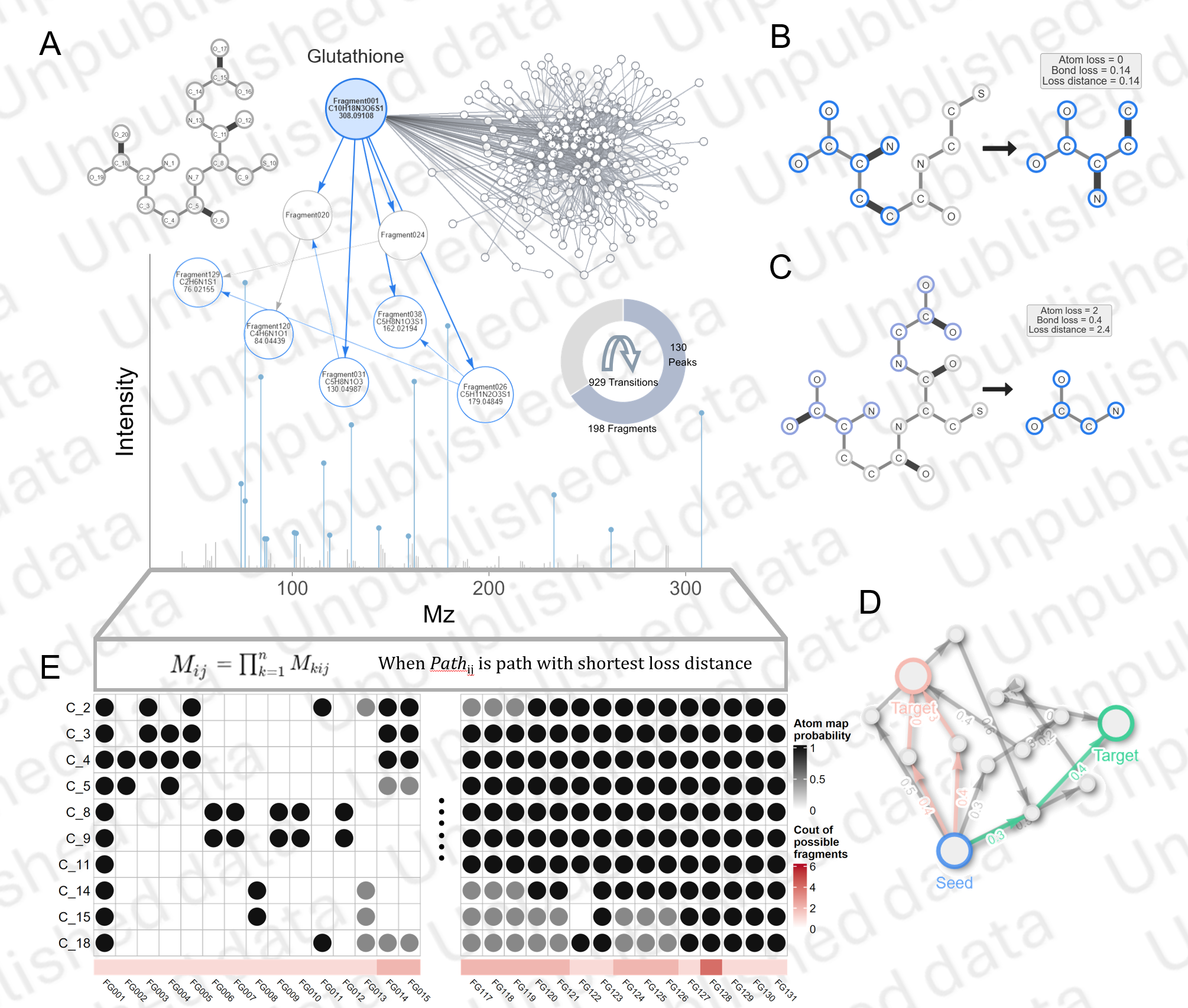
Atom tracing map
Fragment-Atom-Ratio Map
To acquire detailed fragments information, we use a multi-CE scan strategy in MS analysis.
The atom map and isotopic distribution of fragments are integrated as a Fragment-Atom-Ratio Map for isotopomers analysis.
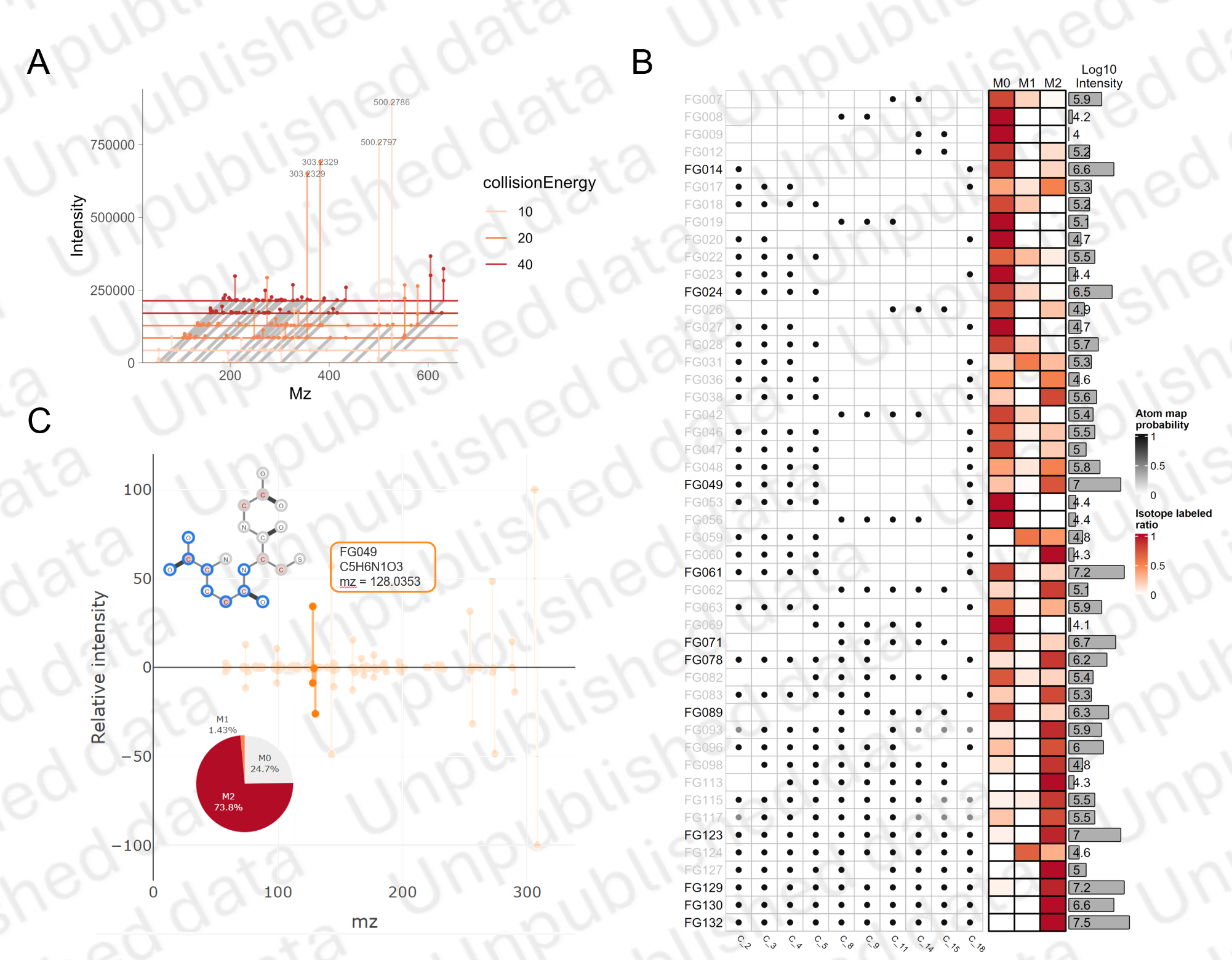
Fragment-Atom-Ratio map
Isotopomers analysis
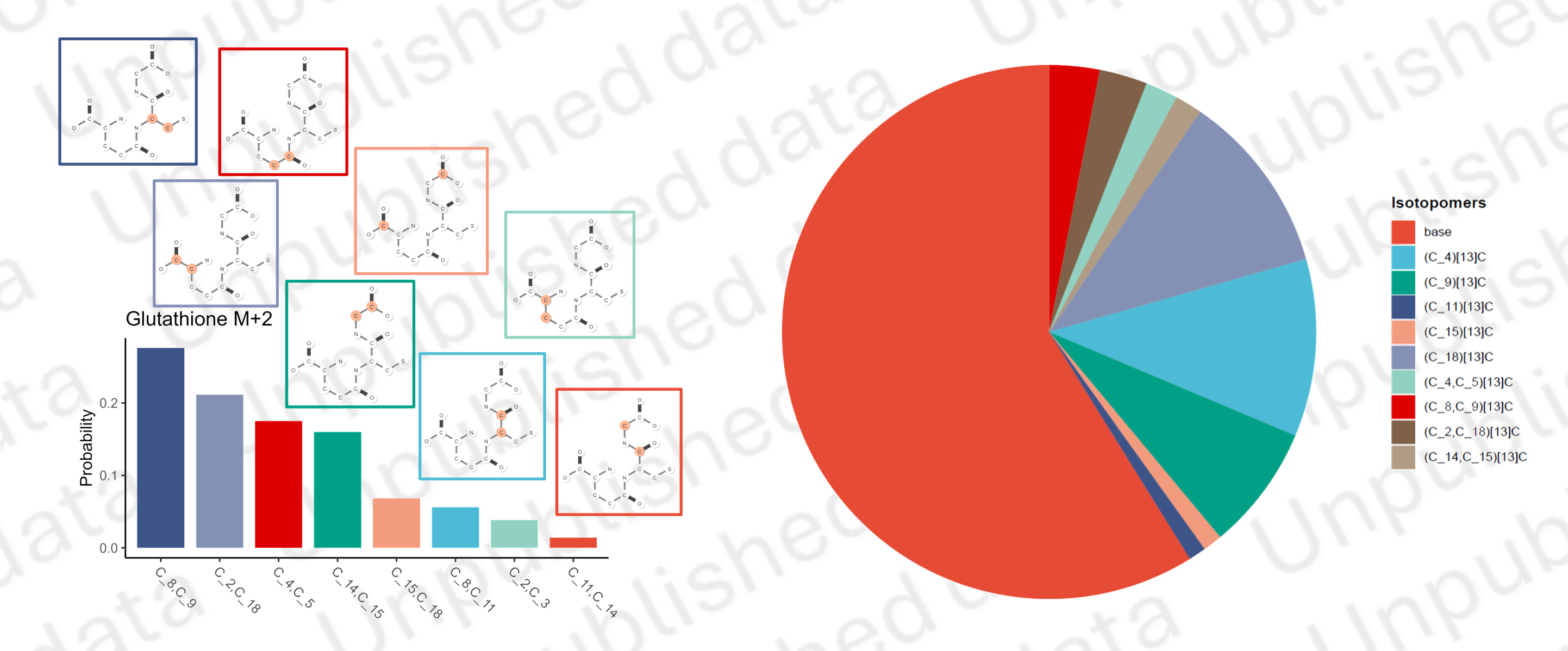
To analyze isotopomers, we first simulate all possible isotopomers and construct a contribution matrix, which represent how much isotopomer contribute to labeled fragments.
In the practical experiment, not all the isotopmers could be solved by detected fragments. In some of situations, some atoms are always bundled in the MS fragmentation, therefore couldn’t be discriminated just by MS data.
Reflected in the FAR map, some of isotopomers show the same pattern of contribution to all labeled fragments (see Figure C). We define these isotopomers as Fragment Split Isotopomers Set (FSIS) to prevent mathematical non-solvability.
These FISS and their contribution matirx to FG are then converted to equation set, which represent the contribution of FSIS leading to detected isotopic distribution of Fragments. Using Nonlinear Programming, we could solve out the probability of FSIS.
Finally, the proportion of natural isotopomers are calculated and deducted. We could calculated the proportion of labeled isotopomers.
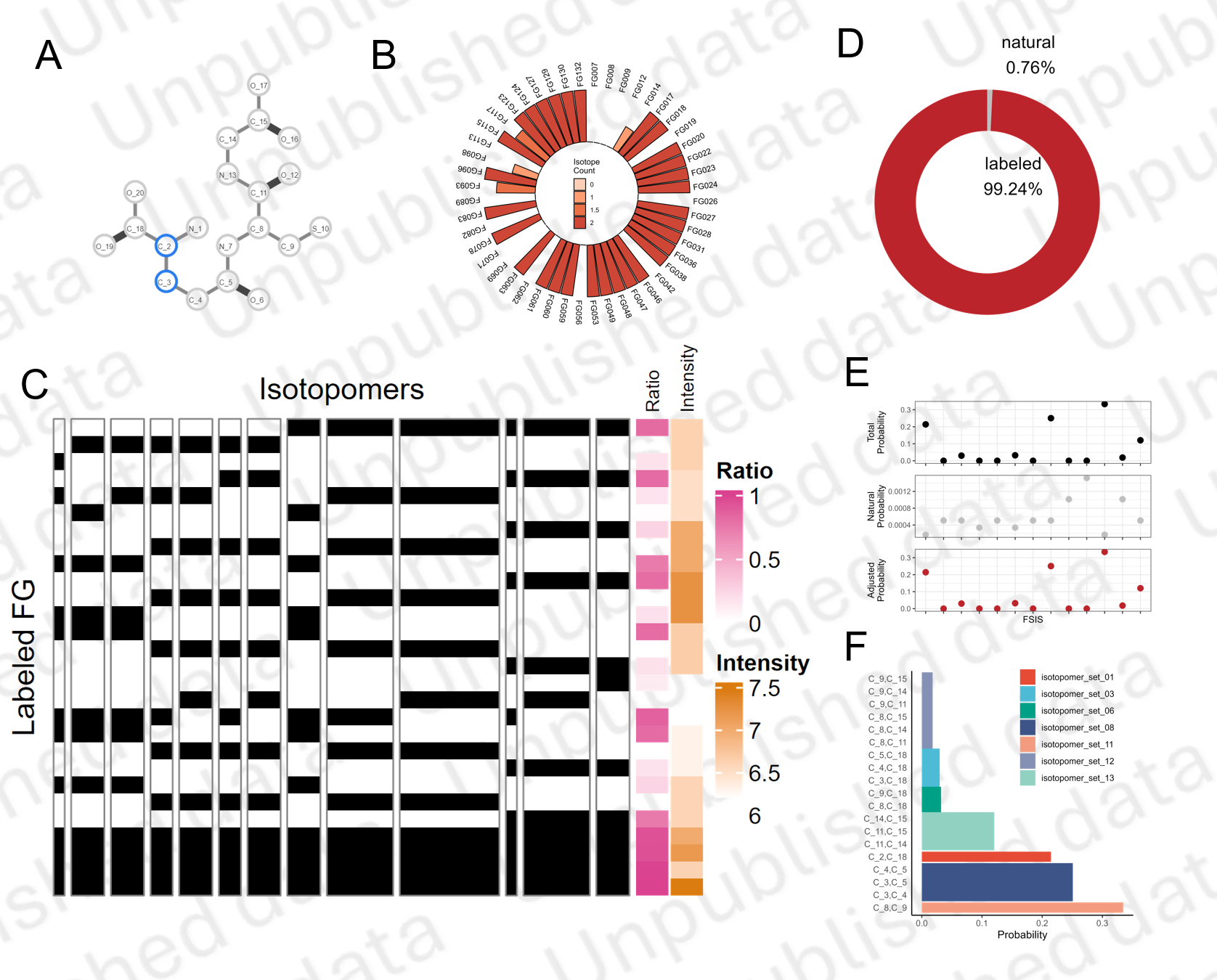
Isotopomers analysis
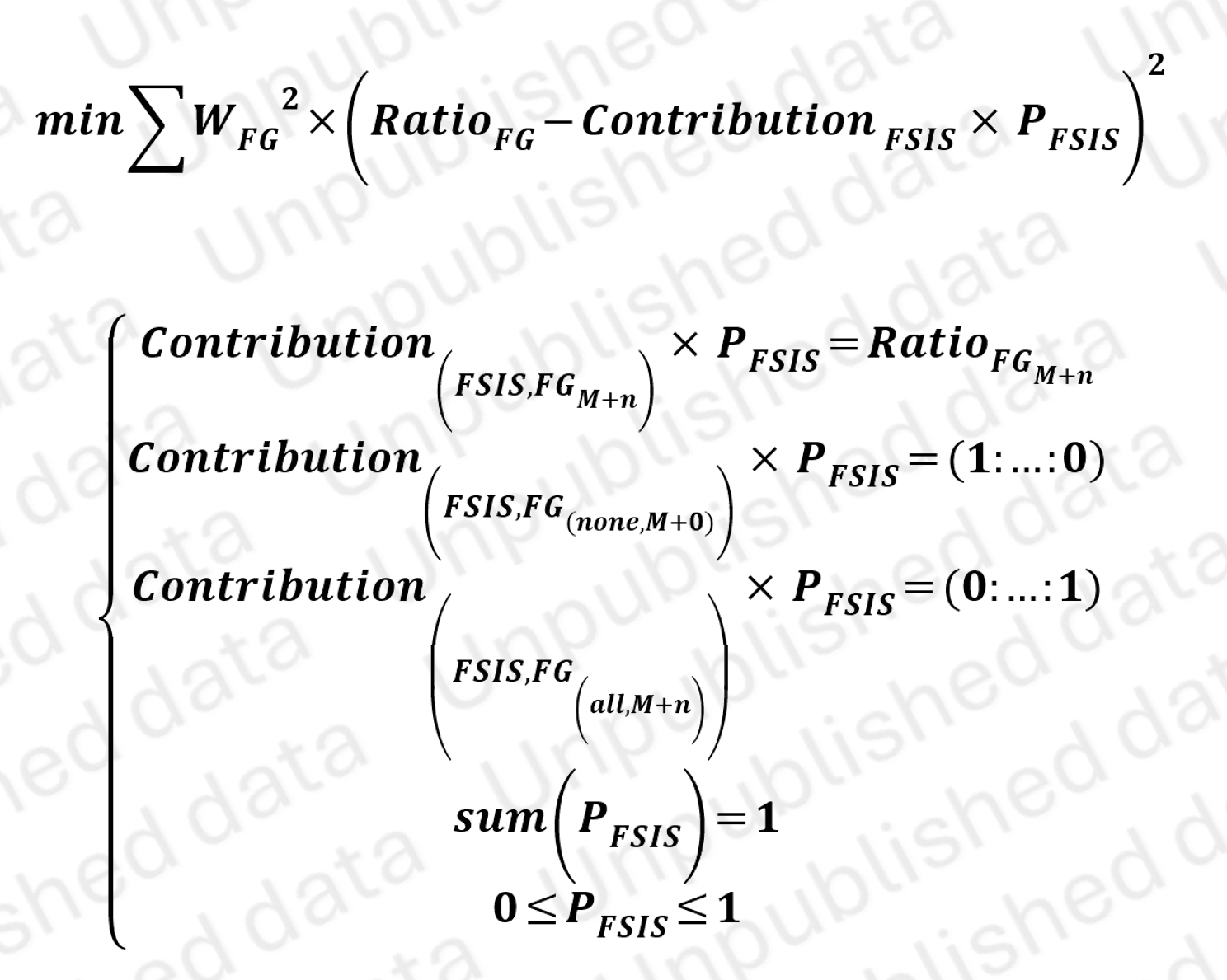
Nonlinear programming to solve isotopomers